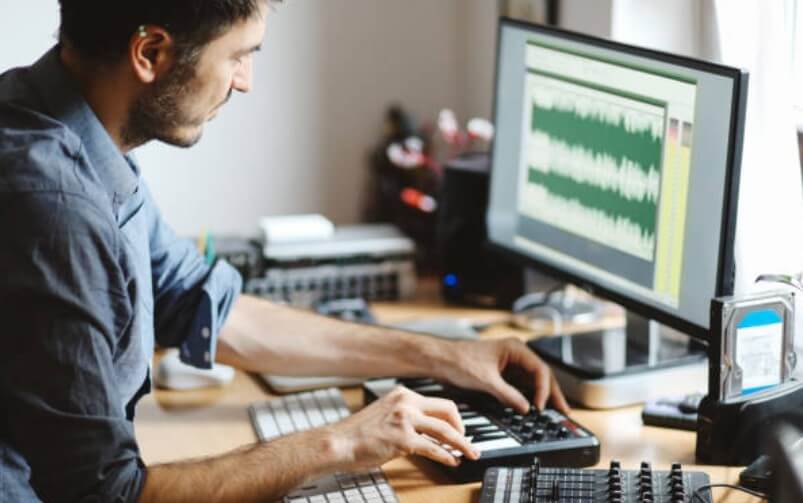
In a final piece of polished music, around 80% of the song comes from the mixing phase. With that said, the other 20% of the mastering process is just as important.
Both mixing and mastering production are complex and fascinating processes that involve several stages.
Even though they sound similar, mixing and mastering are distinct phases that have different purposes for achieving a high-quality final product.
In this article, we will explore the difference between mixing and mastering in music production, shedding light on their individual roles and highlighting their significance.
1. What Is Mixing and Mastering?
In music production, mixing and mastering play huge roles in refining the recorded tracks.
Mixing is the process of balancing the individual tracks in a recording so that they sound good together.
This includes adjusting the levels, panning, EQ, compression, and reverb. The goal of mixing is to create a cohesive sound that highlights the best qualities of the individual tracks.
Mastering is the process of polishing the final mix of a recording.
Mastering includes adjusting the overall levels, EQ, and compression to make the recording sound consistent and to prepare it for distribution.
Mastering can also involve adding limiting to increase the loudness of the recording.
While both processes contribute to achieving exceptional sound quality, they are distinct in their objectives and the stage at which they are performed.
Let’s get into mixing your music and what it involves.
2. The Art of Mixing
Balancing the Elements
Mixing is a creative and technical process where multiple audio tracks are combined, balanced, and adjusted to create a cohesive and harmonious sound.

It involves manipulating individual elements, such as vocals, instruments, and effects, to ensure they blend well together and occupy the desired sonic space.
Through skillful mixing, professional engineers bring out the best in each track and create a balanced mix that captures the intended artistic vision.
Equalization (EQ)
Equalization, commonly referred to as EQ, is a fundamental tool in the mixing process.
It allows engineers to shape the tonal characteristics of each track and eliminate unwanted frequencies or resonances that may muddy the mix.
By adjusting the EQ settings, engineers can emphasize certain frequencies or instruments, correct tonal imbalances, and enhance the overall clarity and definition of the mix.
Dynamic Processing
Dynamic processing techniques, such as compression and limiting, are employed during the audio mixing process.
They aim to control the dynamic range of individual tracks.
Compression helps even out the volume levels and adds sustain to instruments. Limiting, on the other hand, prevents any undesirable audio peaks that may occur during playback.
These tools ensure that all elements in the mix are well-controlled and sit together cohesively.
Spatial Effects
Spatial effects, such as reverb and delay, add depth and dimension to the mix. They create a sense of space.
They simulate different acoustic environments and enhance the perceived distance and positioning of individual instruments or vocals within the mix.
Applying spatial effects, audio engineers can create a more immersive and engaging listening experience.
Automation
Automation is a powerful technique used in mixing to add movement and dynamics to the mix.
It involves making precise adjustments to various parameters, such as volume, panning, and effects, over time.
Automation allows engineers to create gradual or sudden changes in the mix, highlighting specific elements or adding excitement to different sections of the song.
3. The Magic of Mastering
Enhancing the Mix
Mastering is the final step in the music production process. It focuses on enhancing the overall mix. Mastering eventually ensures consistency across tracks and prepares the music for distribution or release.

Mastering engineers work on the stereo mixdown of the song rather than individual tracks.
EQ and Compression
During mastering, EQ and compression are used to refine the tonal balance, dynamic range, and overall cohesiveness of the mix.
The mastering engineer will carefully listen to the entire mix and makes precise adjustments. This is done in order to address any sonic issues or inconsistencies that may be present.
Stereo Enhancement
Stereo enhancement techniques are employed to widen the stereo image and create a more immersive soundstage.
With stereo widening effects, the mastering engineer can give the mix a greater sense of width and spaciousness. This results in a more expansive sound that you hear in radio-ready mixes.
Loudness Maximization
One crucial aspect of mastering is achieving a consistent loudness level across multiple tracks. This makes them sound balanced when played back in a playlist or album.
There are loudness maximization techniques, such as multiband compression and limiting that are used.
These tools and plugins can then achieve optimal loudness while maintaining the dynamic integrity of the music.
Sequencing and Finalization
On top of all the technical adjustments, mastering also involves sequencing and finalizing the order of songs in an album or playlist.
A mastering engineer carefully determines the transitions between tracks.
They’ll also ensure a smooth and coherent listening experience for the audience.
4. The Key Differences Between Mixing and Mastering
While both mixing and mastering involve manipulating audio to improve its quality, there are fundamental differences between the two processes.
Key Differences Between Mixing and Mastering
| Mixing | Mastering |
| Adjusts the levels, panning, EQ, compression, and reverb of individual tracks | Adjusts the overall levels, EQ, and compression of the final mix |
| Creates a cohesive sound that highlights the best qualities of the individual tracks | Polishes the final mix of a recording and prepares it for distribution |
| Can be done by the producer or engineer who mixed the recording | Is typically done by a mastering engineer who specializes in this process |
| Can be a complex and time-consuming process | Is typically a shorter and less complex process |
- Stage: Mixing is performed on individual tracks before they are combined into a final stereo mix, while mastering is applied to the stereo mixdown of the already mixed song.
- Focus: Mixing focuses on achieving a balanced and cohesive sound within individual tracks, whereas mastering concentrates on enhancing the overall mix and preparing it for distribution.
- Tools: Mixing utilizes a wide range of tools, such as EQ, compression, and effects, to shape and balance individual tracks, while mastering employs similar tools but with a broader perspective on the entire mix.
- Objectives: Mixing aims to bring out the best in each track and create a well-balanced mix while mastering aims to ensure consistency, clarity, and optimal loudness across multiple tracks.
Understanding these differences will help you appreciate the intricacies of the music production process. It will also enable you to collaborate effectively with mixing and mastering engineers.
5. To Wrap it Up: Difference Between Mixing and Mastering
In summary, mixing and mastering are two distinct stages in the music production process. With that said, they do contribute to achieving a professional and polished sound.
Mixing involves combining and adjusting individual tracks to create a harmonious mix. Mastering, on the other hand, focuses on enhancing the overall mix, ensuring consistency, and preparing it for distribution.
Both processes require skill, experience, and attention to detail.
A mastering engineer is able to bring out the best in the music and provide an exceptional listening experience for the audience.
Sources:
What Is the Difference Between Mixing and Mastering?
FAQs
Do I need to mix and master my songs?
Yes, both mixing and mastering are essential steps in the music production process to ensure your songs sound polished and professional.
Can I mix and master my own music?
Yes, it’s possible to mix and master your own music. But it’s best to work with professional engineers who have the expertise and specialized equipment to achieve optimal results.
How long does it take to mix and master a song?
The time required for mixing and mastering can vary depending on the complexity of the project and the level of detail required.
Can mastering fix a poorly mixed song?
Mastering can address certain issues in a mix to some extent, but it cannot completely fix a poorly mixed song.
How much does mixing and mastering cost?
In general, mixing and mastering can cost anywhere from a few hundred dollars to a few thousand dollars.
Which is more important, mixing or mastering?
Both mixing and mastering are important, but they serve different purposes.
Which is harder, mixing or mastering?
Mixing is generally considered to be more difficult than mastering. This is because mixing involves more individual elements that need to be balanced. Mastering, on the other hand, is more about polishing the final mix and making small adjustments to the overall sound.

Mike is a skilled musician, guitar technician, and music producer with a passion for audio and gear. He excels in teaching guitar, editing podcasts/videos, and creating captivating soundscapes using cutting-edge hardware, software, and plugins. Mike’s talent and commitment make him highly sought-after in the industry, inspiring fellow musicians worldwide.